Pet Program with Abstract
Description
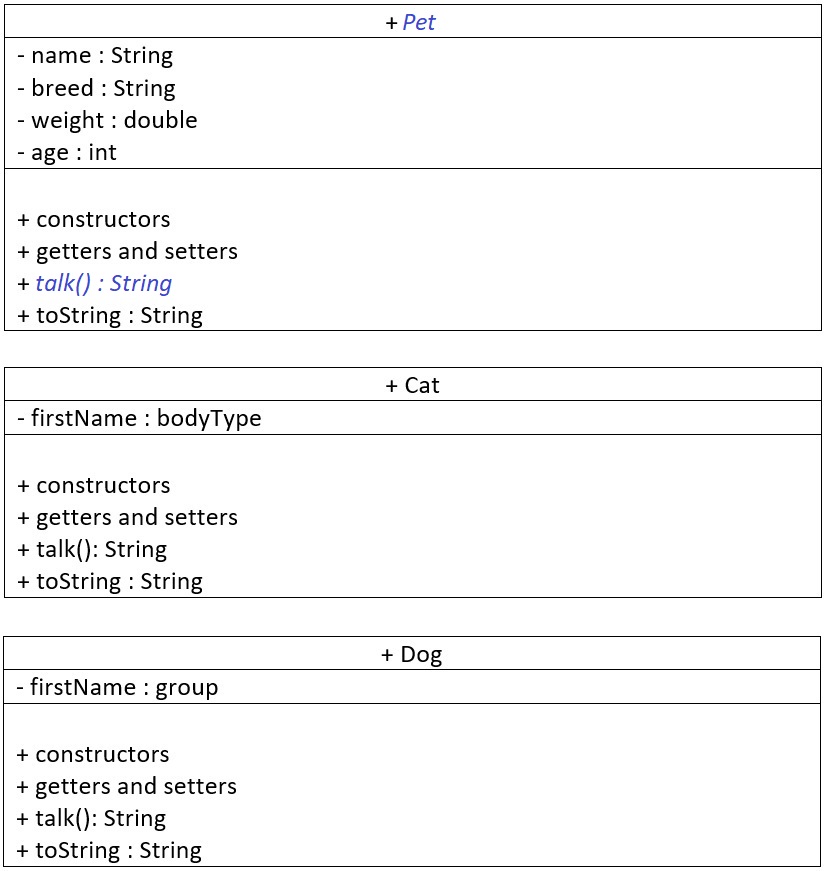
This program incorporates OOP inheritance, polymorphism, and abstract method/class concepts to design classes to represent Pet, Cat, and Dog objects.Each object, either cat or dog, has the name, breed, weight, and age as data members.
A dog object has an additional data member called "group".
A cat object has an additional data member called "body type".
Both dog and cat objects have a talk method.
Cat: Meow, meow, meow
Dog: Woof, woof, woof
Dog: Woof, woof, woof
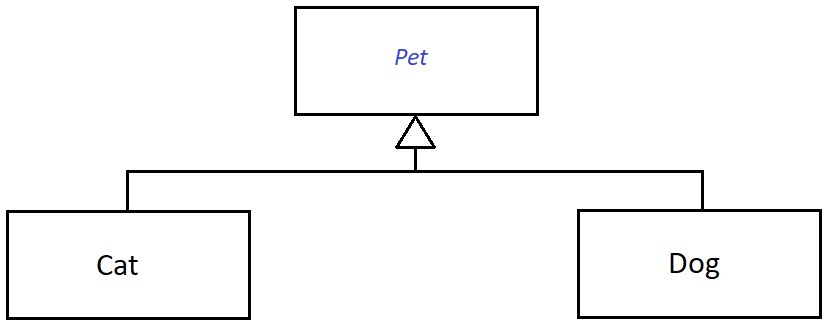
The abstract superclass Pet is an abstract class which defines the common features that apply to any types of pets.
Method talk() is an abstract method.
Data members: name, breed, weight, and age
constructors
getters and setters
talk() method
toString method
constructors
getters and setters
talk() method
toString method
The subclasses Cat and Dog inherit the superclass Pet's features and add additional features.
Cat: body type
Dog: group
Dog: group
Both Cat and Dog classes override the superclass' abstract method talk(). Basically, the Pet's talk() method does not have any implementation. The concrete subclasses determine how to implement it.
Associated Concepts:
OOP - Inheritance
OOP - Polymorphism
OOP - Abstract Method / Class
OOP - Polymorphism
OOP - Abstract Method / Class
Algorithm:
Class diagrams:
Client program:

Client program:
The client program creates an ArrayList of superclass Pet
and adds subclass objects such as dogs and cats to the
ArrayList in random order.
It then invokes the talk() method in the loop using the superclass references.
As we know, the actual subclass object's talk() method is executed.
It then invokes the talk() method in the loop using the superclass references.
As we know, the actual subclass object's talk() method is executed.
Source Code
Superclass Pet class
Subclass Cat class

subclass Dog class

Client program

Sample Run
